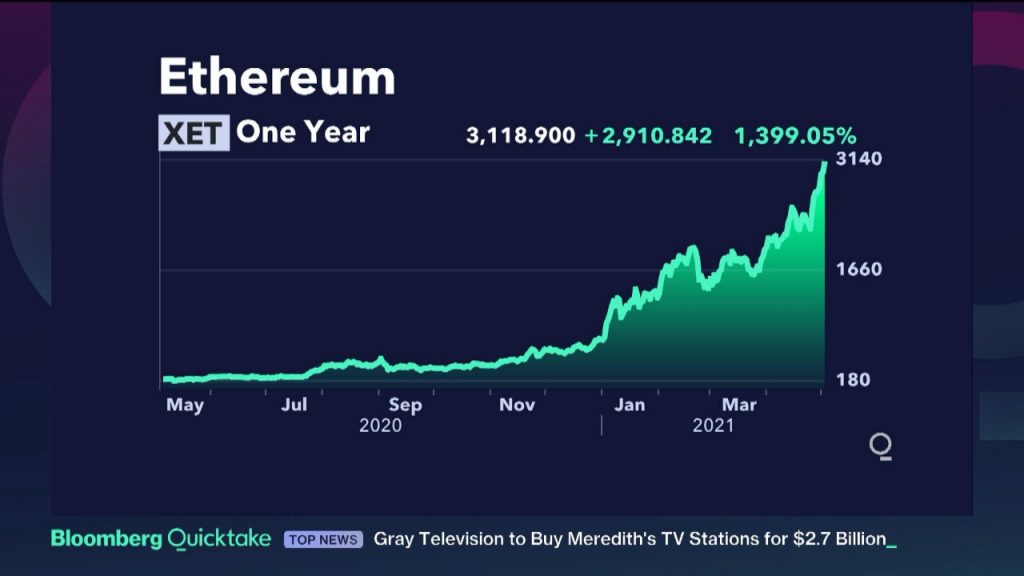
There has been a lot of buzz around the whole crypto space and most people who know about it can’t possibly deny the fact that they’re having major FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out) issues.
Ethereum is a decentralized, most-actively used open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality and is often referred to as the second most popular cryptocurrency, after Bitcoin. Ether (ETH or Ξ) is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. But unlike Bitcoin—and most other virtual currencies—Ethereum is intended to be much more than simply a medium of exchange or a store of value. Instead, Ethereum calls itself a decentralized computing network built on blockchain technology. Let’s unwrap what that means.
Sweet name. What is it?
Ethereum is a blockchain platform with its own cryptocurrency, called Ether (ETH) or Ethereum, and its own programming language, called Solidity.
As a blockchain network, Ethereum is a decentralized public ledger for verifying and recording transactions. The network’s users can create, publish, monetize, and use applications on the platform, and use its Ether cryptocurrency as payment. Insiders call the decentralized applications on the network “dapps.”
How long has it been going on?
Ethereum was launched in July 2015 by a small group of blockchain enthusiasts. They included Joe Lubin, founder of ConsenSys, a blockchain applications developer that uses the Ethereum network. Another co-founder, Vitalik Buterin, is credited with originating the Ethereum concept and now serves as its CEO and public face.
Ethereum was created to enable developers to build and publish smart contracts and distributed applications (dapps) that can be used without the risks of downtime, fraud, or interference from a third party.
Ethereum describes itself as the “world’s programmable blockchain.” It distinguishes itself from Bitcoin as a programmable network that serves as a marketplace for financial services, games, and apps, all of which can be paid for in Ether cryptocurrency and are safe from fraud, theft, or censorship.
How does it work?
Like all cryptocurrencies, Ethereum works based on a blockchain network. A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed public ledger where all transactions are verified and recorded.
It’s distributed in the sense that everyone participating in the Ethereum network holds an identical copy of this ledger, letting them see all past transactions. It’s decentralized therein the network isn’t operated or managed by any centralized entity—instead, it’s managed by all of the distributed ledger holders.
Blockchain transactions use cryptography to keep the network secure and verify transactions. People use computers to “mine,” or solve complex mathematical equations that confirm each transaction on the network and add new blocks to the blockchain that’s at the guts of the system. Participants are rewarded with cryptocurrency tokens. For the Ethereum system, these tokens are called Ether (ETH).
Ether is often used to buy and sell goods and services, like Bitcoin. It’s also seen rapid gains in price over recent years, making it a de-facto speculative investment. But what’s unique about Ethereum is that users can build applications that “run” on the blockchain like software “runs” on a computer. These applications can store and transfer personal data or handle complex financial transactions.
“Ethereum is different from Bitcoin wherein the network can perform computations as a part of the mining process,” says Ken Fromm, director of education and development at the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance. “This basic computational capability turns a store useful and medium of exchange into a decentralized global computing engine and openly verifiable data store.”
Ethereum to the moon
Large, existing network – “The benefits of Ethereum are a tried-and-true network that has been tested through years of operation and billions of useful trading hands,” says Fromm. “It has a large and committed global community and the largest ecosystem in blockchain and cryptocurrency.”
Wide range of functions – Besides getting used as a digital currency, Ethereum also can be wont to process other sorts of financial transactions, execute smart contracts, and store data for third-party applications.
Constant innovation – A large community of Ethereum developers is consistently trying to find new ways to enhance the network and develop new applications. “Because of Ethereum’s popularity, it tends to be the preferred blockchain network for new and exciting (and sometimes risky) decentralized applications,” says Avital.
Avoids intermediaries – Ethereum’s decentralized network promises to let users leave behind third-party intermediaries, like lawyers who write and interpret contracts, banks that are intermediaries in financial transactions, or third-party web hosting services.
Ethereum to Earth
Rising transaction costs – Ethereum’s growing popularity has led to higher transaction costs. Ethereum transaction fees, also referred to as “gas,” hit a record $23 per transaction in February 2021, which is great if you’re earning money as a miner but less so if you’re trying to use the network. This is because unlike Bitcoin, where the network itself rewards transaction verifiers, Ethereum requires those participating within the transaction to hide the fee.
Potential for crypto inflation – While Ethereum has an annual limit of releasing 18 million Ether per year, there’s no lifetime limit on the potential number of coins. This could mean that as an investment, Ethereum might function more like dollars and should not appreciate the maximum amount as Bitcoin, which features a strict lifetime limit on the number of coins.
The steep learning curve for developers – Ethereum is often difficult for developers to select as they migrate from centralized processing to decentralized networks.
Unknown future – Ethereum continues to evolve and improve, and the ongoing development of Ethereum 2.0 holds out the promise of new functions and greater efficiency. However, this major update to the network is creating uncertainty for apps and deals currently in use. “Many new validators are going to be required for Ethereum 2.0 to function,” says DeWaal. “The question is will the migration work? There are tons of latest elements that need to fall under place!”
Environmental concerns – A very large amount of energy is needed for mining bitcoin and Ethereum. In fact, around 1 million dollars worth of electricity is consumed in mining them daily.
Ethereum 2.0
Currently, the major problem is that Ethereum, like most cryptocurrencies, relies on a computational competition called Proof-of-Work(PoW).
To explain it simply, proof-of-work is basically a race between computers to validate a transaction and out of the thousands of computers that participate in this race, only one gets to validate the transaction and essentially, gets some transaction fees in return. What this race does is that it leads to wastage of energy by the other computers that might not have been as fast as the one that finally validates a transaction.
To solve this, Ethereum 2.0 will be working on a totally different algorithm under which it’ll rely on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) for its transactions, potentially reducing the amount of electricity consumed for mining Ethereum by 99%.
Simply explained, PoS eliminates this race to verify a transaction. Computers basically take part in a lucky draw whose winner is decided by the chain itself. The winner then validates the transaction and gets a much smaller reward for having to consume much less electricity. To volunteer in this lucky draw, you have to stake some of your Ether coins into storage, and if you cheat during a transaction, you are penalized and some of your coins are taken away by the person who spots the fraud. In fact, to keep the lucky draw fair the more ether you stake, the higher your chance of getting picked the winner.
Other than that, one of the biggest reasons for the upgrade to Ethereum 2.0 is scalability. With Ethereum 1.0, the network can only support around 30 transactions per second; this causes delays and congestion. Ethereum 2.0 promises up to 100,000 transactions per second. This increase is going to be achieved through the implementation of shard chains. Also, Ethereum 2.0 requires a minimum of 16,384 validators, making it much more decentralized—and hence, secure.
Conclusion
After the recent news of Bitcoin being legalised in El Salvador, we can’t really comment about what’s in store for Ethereum. But, coming back to the title, I leave that for you to decide whether or not Ethereum should be legalised.
The Economic Burden of Gun Violence in USA
Trigger warning – The following piece of writing contains mentions of gun violence and its…
Conspicuous Consumption
The Prisoner’s Dilemma
Game theory has the prisoner’s dilemma as one of its most popular examples, whose implications…
Looking into Negative Prices of Oil Futures: An FIC Hindu Report
The Simpson’s Paradox
The Simpson’s paradox, famously known as the Yule-Simpson effect is a compelling demonstration of how…
The Paradox of Unanimity
On one end of the spectrum lies the idea of majority consensus, which drives the…